JavaScript CheatSheet
Scroll To:
Copy Code
//On page script
<script type="text/javascript"> ...
</script>
// Include external JS file
<script src="filename.js"></script>
// Delay - 1 second timeout
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("Abdullah Ansari"); //run after one second
}, 1000);
// Functions
function addNumbers(a, b) {
return a + b; ;
}
x = addNumbers(1, 2);
// Edit DOM element
document.getElementById("elementID").innerHTML = "Hello World!";
// Output
console.log(Abd); // write to the browser console
document.write(Abd); // write to the HTML
alert(Abd); // output in an alert box
confirm("Save Data?"); // yes/no dialog, returns true/false depending on user click
prompt("Your age?","0"); // input dialog. Second argument is the initial value
// Comments
/* Multi line
comment */
// One line
Copy Code
var variable:
var: It can be redeclared and its value can be reassigned,
but only inside the context of a function. When the JavaScript code is run,
variables defined using var are moved to the top.
const Variable:
const: const variables in JavaScript cannot be
used before they appear in the code.
They can neither be reassigned values,
that is, their value remains fixed throughout
the execution of the code, nor can they be redeclared.
let Variable:
let: The let variable, like const, cannot be redeclared.
But they can be reassigned a value.
var a; // variable
let b = "init"; // string
let c = "Hi" + " " + "Abd"; // = "Hi Abd"
let d = 1 + 2 + "3"; // = "33" number + string becomes string
let e = [2,3,5,8]; // array
let f = false; // boolean
let g = /()/; // RegEx
let h = function(){}; // function object
const PI = 3.14; // constant
var a = 1, b = 2, c = a + b; // one line
let z = 'zzz'; // block scope local variable
// Strict mode
"use strict"; // Use strict mode to write secure code
x = 1; // Throws an error because variable is not declared
// Values
false, true // boolean
18, 3.14, 0b10011, 0xF6, NaN // number
"flower", 'John' // string
undefined, null , Infinity // special
Copy Code
let age = 18; // number
let name = "Jane"; // string
let name2 = {first:"Abdullah", last:"Ansari"}; // object
let truth = false; // boolean
let sheets = ["React","Vue","JS"]; // array
let a; typeof a; // undefined
let a = null; // value nul
// Objects
var student = { // object name
firstName:"Abdullah", // list of properties and values
lastName:"Ansari",
age:18,
height:170,
fullName : function() { // object function
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
};
student.age = 19; // setting value
student[age]++; // incrementing
name = student.fullName(); // call object function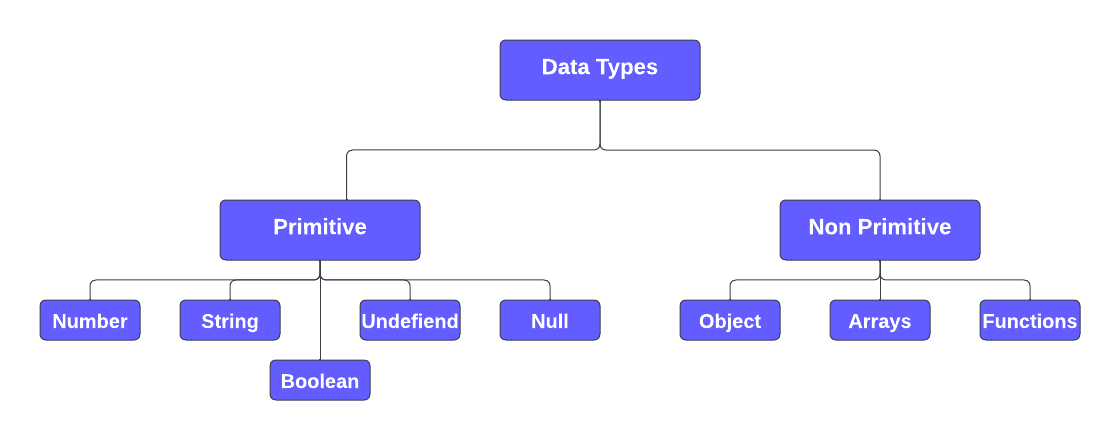
Copy Code
1- Fundamental Operators:
a = b + c - d; // addition, substraction
a = b * (c / d); // multiplication, division
x = 100 % 48; // modulo. 100 / 48 remainder = 4
a++; b--; // postfix increment and decrement
2- Bitwise Operators:
&: The bitwise AND operator returns a 1 in every bit position where both operands'
corresponding bits are 1.
|: The bitwise OR operator (|) returns a 1 in each
bit position where either or both operands'
corresponding bits are 1.
~: The bitwise NOT operator reverses the operand's bits.
It turns the operand into a 32-bit signed integer,
just like other bitwise operators.
^: The bitwise XOR operator () returns a 1 in each bit position
where the corresponding bits of both operands are 1s but not both.
<<: The left shift operator shifts the first operand
to the left by the provided number of bits.
Extra bits that have been relocated to the left are discarded.
From the right, zero bits are shifted in.
>>: The right shift operator (>>) moves the first operand
to the right by the provided number of bits.
Extra bits that have been relocated to the right are discarded.
The leftmost bit's copies are shifted in from the left.
The sign bit (the leftmost bit) does not change since the new
leftmost bit has the same value as the old leftmost bit.
As a result, the term "sign-propagating" was coined.
3- Comparison Operators:
a == b // equals
a === b // strict equal
a != b // not equal
a != b // unequal
a !== b // strict unequal
a < b a > b // less and greater than
a <= b a >= b // less or equal, greater or eq
4- Logical Operators:
! // logical not
a && b // logical and
a || b // logical orCopy Code
if ((age >= 14) && (age < 19)) { // logical condition
status = "Eligible."; // executed if condition is true
} else { // else block is optional
status = "Not eligible."; // executed if condition is false
}Copy Code
switch (new Date().getDay()) { // input is current day
case 6: // if (day == 6)
text = "Saturday";
break;
case 0: // if (day == 0)
text = "Sunday";
break;
default: // else...
text = "Whatever";
} Copy Code
for loop:
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
console.log("Run",i);
}
while Loop:
let i = 1; // initialize
while (i < 100) { // enters the cycle if statement is true
i *= 2; // increment to avoid infinite loop
console.log(i + ", ");
}
do while Loop:
let i = 1; // initialize
do { // enters cycle at least once
i *= 2; // increment to avoid infinite loop
console.log(i + ", ");
} while (i < 100) // repeats cycle if statement is true at the end
break:
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 5) { break; } // stops and exits the cycle
console.log(i + ", "); // last output number is 4
}
continue:
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 5) { continue; } // skips the rest of the cycle
document.write(i + ", "); // skips 5
}
Copy Code
var arr = ["Shirt", "Pent", "Shoes"];
var arr = new Array("Shirt", "Pent", "Shoes"); // declaration
alert(arr[1]); // access value at index, first item being [0]
arr[0] = "Lamp"; // change the first item
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // parsing with array.length
console.log(arr[i]);
Methods:
1- arr.toString(); // convert to string: results "Shirt,Pent,Shoes"
2- arr.join(" * "); // join: "Shirt * Pent * Shoes"
3- arr.pop(); // remove last element
4- arr.push("Hoodie"); // add new element to the end
5- arr[arr.length] = "Hoodie"; // the same as push
6- arr.shift(); // remove first element
7- arr.unshift("Hoodie"); // add new element to the beginning
8- delete arr[0]; // change element to undefined (not recommended)
9- arr.splice(2, 0, "Pug", "Boxer"); /* add elements
(where, how many to remove, element list)*/
10- var animals = arr.concat(cats,birds); /* join two
arrays (arr followed by cats and birds)*/
11- arr.slice(1,4); // elements from [1] to [4-1]
12- arr.sort(); // sort string alphabetically
13- arr.reverse(); // sort string in descending order
14- x.sort(function(a, b){return a - b}); // numeric sort
15- x.sort(function(a, b){return b - a}); // numeric descending sort
16- highest = x[0]; /* first item
in sorted array is the lowest (or highest) value*/
17- x.sort(function(a, b){return 0.5 - Math.random()}); // random order sort Copy Code
function nameOfTheFunction(parameterOne,
parameterTwo, parameterThree,
parameterFour,....,parameterN) {
// Job or Task of the function
}
Functions For Throwing Data As Output:
1- prompt(): This function is used for creating
a dialogue box for taking input from the user.
2- alert(): This function is used for outputting
information in an alert box in the browser window.
3- console.log(): This function is used for writing
data to the browser's console and is used for
the purpose of debugging code by developers.
4- document.write(): This function is used for writing
straight to our HTML document.
5- confirm(): This function is used for opening up
a yes or no dialogue box and for returning a
boolean value depending upon the user's click
Global Functions: Every browser that can run JavaScript
has a set of global functions built-in.
1- parseFloat(): This function is used for parsing the
argument passed to it and returning a floating-point number.
2- parseInt(): This function is used for parsing
the argument passed to it and returning an integral number.
3- encodeURI(): This function is used for
encoding a URI into a UTF-8 encoding scheme.
4- decodeURI(): This function is used for
decoding a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI)
made by encodeURI() function or similar functions.
5- encodeURIComponent(): This function is used for the same
purpose as encodeURI() only for URI components.
6- decodeURIComponent(): This function is used
for decoding a URI component.
7- isNaN(): This function is used for determining
if a given value is Not a Number or not.
8- Number(): This function is used for returning a
number converted from what is passed as an argument to it.
9- eval(): This function is used for evaluating
JavaScript programs presented as strings.
10- isFinite(): This function is used for determining
if a passed value is finite or not.Copy Code
Scope: The accessibility or visibility of variables
in JavaScript is referred to as scope.
That is, which sections of the program can access
a given variable and where the variable can be seen.
Global Scope: The global scope includes any variable
that is not contained within a function or
block (a pair of curly braces).
Global scope variables can be accessed from anywhere in the program.
var hello = 'Hello!';
function sayHello() {
console.log(hello);
}
// 'Hello!' gets logged
sayHello();
Local or Function Scope: Variables declared inside a
function are local variables.
They can only be accessed from within that function;
they are not accessible from outside code.
function sayHello() {
var hello = 'Hello!';
console.log(hello);
}
// 'Hello!' gets logged
sayHello();
Block Scope: Unlike var variables,
let and const variables can be scoped to the nearest pair
of curly brackets in ES6.
They can't be reached from outside that pair of curly braces,
which means they can't be accessed from the outside.
{
let hello = 'Hello!';
var language = 'Urdu';
console.log(hello); // 'Hello!' gets logged
}
console.log(language); // 'Urdu!' gets logged
console.log(hello); // Uncaught ReferenceError: hello is not definedCopy Code
Scope Chain: When a variable is used in JavaScript,
the JavaScript engine searches the current scope for the variable's value.
If it can't find the variable in the inner scope,
it will look into the outer scope until it finds it or reaches the global scope.
If it still can't identify the variable,
it will either return an error or implicitly declare
the variable in the global scope (if not in strict mode)
let a = 'a';
function foo() {
let b = 'b';
console.log(b); // 'b' gets logged
console.log(a); // 'a' gets logged
randomNumber = 33;
console.log(randomNumber); // 33 gets logged
}
foo();
When the function foo() is called,
the JavaScript engine searches for the 'b' variable
in the current scope and finds it.
Then it looks for the 'a' variable in the current scope,
which it can't find, so it moves on to the outer scope,
where it finds it (i.e global scope).
After that, we assign 33 to the 'randomNumber' variable,
causing the JavaScript engine to search for it
first in the current scope, then in the outer scope.
If the script isn't in strict mode,
the engine will either create a new variable
called randomNumber and assign 33 to it, or
it will return an error (if not in strict mode).
As a result, the engine will traverse
the scope chain till the time when a variable is found.Copy Code
Prior to executing the code, the interpreter appears
to relocate the declarations of functions, variables,
and classes to the top of their scope using a process
known as Hoisting in JavaScript. Functions can be
securely utilized in code before they have been
declared thanks to hoisting. Variable and class
declarations are likewise hoisted, allowing them
to be referenced prior to declaration. It should
be noted that doing so can result in unforeseen
mistakes and is not recommended.
Function Hoisting: Hoisting has the advantage of
allowing you to use a function before declaring
it in your code as shown in the code snippet given below.
Without function hoisting, we would have to first write
down the function display and only then can we call it.
display("Abdullah");
function display(inputString) {
console.log(inputString); // 'Abdullah' gets logged
}
Variable Hoisting: You can use a variable in code before
it is defined and/or initialized because hoisting works
with variables as well. JavaScript, however,
only hoists declarations, not initializations!
Even if the variable was initially initialized
then defined, or declared and initialized on the same line,
initialization does not occur until the associated line of
code is run. The variable has its default
initialization till that point in the execution
is reached (undefined for a variable declared
using var, otherwise uninitialized).
console.log(x) /*'undefined' is logged
from hoisted var declaration (instead of 7)*/
var x // Declaration of variable x
x = 7; // Initialization of variable x to a value 7
console.log(x); /* 7 is logged post the
line with initialization's execution.*/Copy Code
Escape Sequences or Escape Characters:
1- \' — Single quotes
2- \" — Double quotes
3- \t — Horizontal tab
4- \v — Vertical tab
5- \\ — Backslash
6- \b — Backspace
7- \f — Form feed
8- \n — Newline
9- \r — Carriage return
String methods:
1- toLowerCase() — This method is used for converting strings to lower case.
2- toUpperCase() — This method is used for converting strings to upper case
3- charAt() — This method is used for returning the character at a
particular index of a string
4- charCodeAt() — This method is used for returning to us the
Unicode of the character at a given index
5- fromCharCode() — This method is used for returning a string
made from a particular sequence of UTF-16 code units
6- concat() — This method is used for concatenating or
joining multiple strings into a single string
7- match() — This method is used for retrieving the matches
of a string against a pattern string which is provided
8- replace() — This method is used for finding and
replacing a given text in the string
9- indexOf() — This method is used for providing the index
of the first appearance of a given text inside the string
10- lastIndexOf() — This method is similar to the indexOf()
methods and only differs in the fact that it searches for
the last occurrence of the character and searches backwards
11- search() — This method is used for executing a search
for a matching text and returning the index of the searched string
12- substr() — This method is pretty much the same as the
slice() method but the extraction of a substring in it
depends on a given number of characters
13- slice() — This method is used for extracting an
area of the string and returning it
14- split() — This method is used for splitting a string
object into an array of strings at a particular index
15- substring() — Even this method is almost the same as
the slice() method but it does not allow negative positions
16- valueOf() — This method is used for returning the
primitive value (one without any properties or methods)
of a string object.Copy Code
/*LEXICAL SCOPE: when a inner function is access the variable of outer function
then its called lexical scope*/
function Outer() {
var a = 10;
function inner() {
return a;
}
return inner();
}
console.log(Outer());Copy Code
/*Clousre SCOPE: when a inner function is access the variable of outer function and
remember the variables simply we can say that the variable of outer function
is access in inner function on run time*/
function Outer() {
var a = 10;
function inner() {
return a;
}
return inner;
}
let innerFunction= Outer();
console.log(innerFunction());Copy Code
Node Properties:
1- attributes — Gets a live list of all the
characteristics associated with an element.
2- baseURI — Returns an HTML element's absolute base URL.
3- childNodes — Returns a list of the child nodes of an element.
4- firstChild — Returns the element's first child node.
5- lastChild — An element's final child node
6- nextSibling — Returns the next node in
the same node tree level as the current node.
7- nodeName —Returns a node's name.
8- nodeType — Returns the node's type.
9- nodeValue — Sets or returns a node's value.
10- ownerDocument — This node's top-level document object.
11- parentNode — Returns the element's parent node.
12- previousSibling — Gets the node that comes before the current one.
13- textContent — Sets or returns a node's and its descendants' textual content.
Node Methods:
1- cloneNode() is a function that duplicates an HTML element.
2- compareDocumentPosition() — Compares two elements' document positions.
3- getFeature() returns an object that implements the APIs of a feature.
4- hasAttributes() — If an element has any attributes,
it returns true; otherwise, it returns false.
5- hasChildNodes() — If an element has any child nodes,
it returns true; otherwise, it returns false.
6- insertBefore() — Adds a new child node to the
left of an existing child node.
7- isDefaultNamespace() returns true if a given
namespaceURI is the default, and false otherwise.
8- isEqualNode() — Determines whether two elements are the same.
9- isSameNode() — Determines whether two elements belong to the same node.
10- isSupported() — Returns true if the element supports the provided feature.
11- lookupNamespaceURI() — Returns the namespace URI for a specific node.
12- lookupPrefix — If the prefix for a given
namespace URI is present,
lookupPrefix() returns a DOMString containing it.
13- normalize() — In an element, joins
neighboring text nodes and removes empty text nodes.
14- removeChild() — Removes a child node from
an element using the Child() method.
15- replaceChild() — In an element, this
function replaces a child node.
16- appendChild() — Adds a new child node as
the last child node to an element.
Element Methods:
1- getAttribute() — Returns the value of an
element node's provided attribute.
2- getAttributeNS() returns the string value
of an attribute with the namespace and name supplied.
3- getAttributeNode() — Returns the attribute node supplied.
4- getAttributeNodeNS() — Returns the attribute
node for the specified namespace and name for the attribute.
5- getElementsByTagName() — Returns a list of
all child elements whose tag name is supplied.
6- getElementsByTagNameNS() — Returns a live
HTMLCollection of items belonging to the
provided namespace with a certain tag name.
7- hasAttribute() — If an element has any attributes,
it returns true; otherwise, it returns false.
8- hasAttributeNS() returns true or false depending
on whether the current element in a particular
namespace has the supplied attribute.
9- removeAttribute() — Removes an element's supplied attribute.
10- removeAttributeNS() — Removes an attribute
from an element in a specific namespace.
11- setAttributeNode() — Sets or modifies an attribute node.
12- setAttributeNodeNS() — Sets a new namespaced
attribute node to an element with setAttributeNodeNS().Copy Code
Numbers Properties:
1- MAX VALUE — The maximum numeric value that
JavaScript can represent.
2- NaN — The "Not-a-Number" value is NaN.
3- NEGATIVE INFINITY – The value of Infinity is negative.
4- POSITIVE INFINITY – Infinity value that is positive.
5- MIN VALUE — The smallest positive numeric value
that JavaScript can represent.
Numbers Methods:
1- toString() — Returns a string representation of an integer.
2- toFixed() — Returns a number's string with a
specified number of decimals.
3- toPrecision() — Converts a number to a string
of a specified length.
4- valueOf() — Returns a number in its original form.
5- toExponential() — Returns a rounded number
written in exponential notation as a string.
Maths Properties:
1- E — Euler's number is E.
2- SQRT1_2 — 1/2 square root
3- SQRT2 stands for square root of two.
4- LOG2E — E's base 2 logarithm
5- LN2 — The natural logarithm of 2 is LN2.
6- LN10 — The natural logarithm of ten is LN10.
7- LOG10E — E's base ten logarithm
8- PI — PI stands for Pianistic Integer.
Maths Methods:
1- exp(x) — Ex's value
2- floor(x) — x's value rounded to the nearest integer.
3- log(x) — The natural logarithm (base E) of x is log(x).
4- abs(x) — Returns the value of x in its absolute (positive) form.
5- acos(x) — In radians, the arccosine of x.
6- asin(x) — In radians, the arcsine of x.
7- pow(x,y) — x to the power of y
8- random() — Returns a number between 0 and 1 at random.
9- round(x) — Rounds the value of x to the nearest integer.
10- sin(x) — The sine of x is sin(x) (x is in radians)
11- sqrt(x) — x's square root
12- tan(x) — The angle's tangent
13- atan(x) is the numeric value of the arctangent of x.
14- atan2(y,x) — Arctangent of its arguments' quotient
15- ceil(x) — x's value rounded to the next integer
16- cos(x) – The cosine of x is cos(x) (x is in radians)
17- max(x,y,z,...,n) — Returns the highest-valued number.
18- min(x,y,z,...,n) — The number with the lowest
value is the same as the number with the highest value.Copy Code
Setting Dates:
1- Date() — Returns a new date object that contains the current date and time.
2- Date(1993, 6, 19, 5, 12, 50, 32) — We can create
a custom date object with the pattern as
Year, month, day, hour, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds
are represented by the numbers. Except for the
year and month, we can omit anything we like.
3- Date("1999-12-22") — Date as a string declaration
Getting the values of Time and Date:
1- getDate() returns the month's day as a number (1-31)
2- getTime() — Get the milliseconds since January 1, 1970
3- getUTCDate() returns the month's day (day) in the
supplied date in universal time
(also available for day, month, full year, hours, minutes etc.)
4- getMilliseconds() — This function returns the milliseconds (0-999)
5- getMinutes() — Returns the current minute (0-59)
6- getMonth() returns the current month as a number (0-11)
7- parse — It returns the number of milliseconds
since January 1, 1970 from a string representation of a date.
8- getDay() returns a number representing the weekday (0-6)
9- getFullYear() returns the current year as a four-digit value (yyyy)
10- getHours() — Returns the current hour (0-23)
11- getSeconds() — Returns the second number (0-59)
Setting a Part of the Dates:
1- setDate() — Returns the current date as a number (1-31)
2- setFullYear() — This function sets the year (optionally month and day)
3- setMonth() — This function sets the month (0-11)
4- setSeconds() — This function sets the seconds (0-59)
5- setTime() — This function is used to
set the time (milliseconds since January 1, 1970)
6- setMinutes() — This function sets the minutes (0-59)
7- setUTCDate() — According to universal time, sets the
day of the month for a given date (also available
for day, month, full-year, hours, minutes etc.)
8- setHours() — Changes the time (0-23)
9- setMilliseconds() — This function sets the milliseconds (0-999)Copy Code
list of Window properties that JavaScript can take into account:
1- history — Provides the window's History object.
2- innerHeight — The content area of a window's inner height.
3- innerWidth — The content area's inner width.
4- closed — Returns true or false depending on whether or not a
window has been closed.
5- pageXOffset — The number of pixels offset from the centre of the page.
The current document has been horizontally scrolled.
6- pageYOffset — The number of pixels offset from the centre of the page.
The document has been vertically scrolled.
7- navigator — Returns the window's Navigator object.
8- opener — Returns a reference to the window that created the window.
9- outerHeight — A window's total height, including toolbars and scrollbars.
10- outerWidth — A window's outside width, including toolbars and scrollbars.
11- defaultStatus — Changes or restores the default text in a window's status bar.
12- document — Returns the window's document object.
13- frames — All <iframe> elements in the current window are returned by frames.
14- length — Determine how many iframe> elements are in the window.
15- location — Returns the window's location object.
16- name — Sets or retrieves a window's name.
17- parent — The current window's parent window is called parent.
18- screen — Returns the window's Screen object.
19- screenLeft — The window's horizontal coordinate (relative to the screen)
20- screenTop — The window's vertical coordinate.
21- self — Returns the window that is currently open.
22- status — Changes or restores the text in a window's status bar.
23- top — Returns the browser window that is currently at the top of the screen.
24- screenX — Identical to screenLeft, but required by some browsers
25- screenY — Identical to screenTop, but required by some browsers
The JavaScript methods which can work on the user's browser window:
1- alert() — Shows a message and an OK button in an alert box.
2- setInterval() — Calls a function or evaluates an expression at
intervals defined by the user.
3- setTimeout() — After a specified interval,
calls a function or evaluates an expression.
4- clearInterval() — Removes a timer that was
started with setInterval() ()
5- clearTimeout() — Removes the timer that was
set with setTimeout() ()
6- open() — This method creates a new browser window.
7- print() — Prints the current window's content.
8- blur() — Removes the current window's focus.
9- moveBy() — Repositions a window with respect to its
present position.
10- moveTo() — This function moves a window to a
specific location.
11- close() — This function closes the currently open window.
12- confirm() — Shows a dialogue box with a message and
buttons to OK and Cancel.
13- focus() — Sets the current window's focus.
14- scrollBy() — Scrolls the document by a certain amount of pixels.
15- scrollTo() — Scrolls the document to the supplied coordinates
with the scrollTo() method.
16- prompt() — Shows a conversation window asking for
feedback from the visitor.
17- resizeBy() — Resizes the window by the number of pixels supplied.
18- resizeTo() — Resizes the window to the width and height supplied.
19- stop() — This function prevents the window from loading.
list of Screen properties that JavaScript can take into account:
1- height — The screen's entire height.
2- pixelDepth — The screen's color resolution in bits per pixel.
3- width — The screen's entire width.
4- colorDepth — Gets the color palette's bit depth for showing images.
5- availableHeight — Returns the screen's height (excluding the Windows Taskbar).
6- availableWidth — Returns the screen's width (excluding the Windows Taskbar)Copy Code
Mouse Events:
1- onclick – When a user clicks on an element, an event is triggered.
2- oncontextmenu — When a user right-clicks on an element,
a context menu appears.
3- ondblclick — When a user double-clicks on an element,
it is called ondblclick.
4- onmousedown — When a user moves their mouse over an element,
it is called onmousedown.
5- onmouseenter — The mouse pointer is moved to a certain element.
6- onmouseleave — The pointer leaves an element.
7- onmousemove — When the pointer is over an element, it moves.
8- onmouseover — When the cursor is moved onto an element or one of
its descendants, the term onmouseover is used.
9- onmouseout — When the user moves the mouse cursor away from an
element or one of its descendants, it is called onmouseout.
10- onmouseup — When a user releases a mouse button while
hovering over an element, it is known as onmouseup.
Form Events:
1- onblur — When an element loses focus, it is called onblur.
2- onchange — A form element's content changes.
(for the input>, select>, and textarea> elements)
3- onfocus – An aspect is brought into focus.
4- onfocusin — When an element is ready to become the centre of attention.
5- onfocusout —The element is about to lose focus.
6- oninput — When a user inputs something into an element, it's called oninput.
7- oninvalid — If an element isn't valid, it's called oninvalid.
8- onreset — The state of a form is reset.
9- onsearch — A user enters text into a search field (for input="search">).
10- onselect — The user chooses some text (input> and textarea>).
11- onsubmit — A form is filled out and submitted.
Drag Events:
1- ondrag — When an element is dragged, it is called ondrag.
2- ondragend — The element has been dragged to its
final position.
3- ondragenter — When a dragged element enters a
drop target, it is called ondragenter.
4- ondragleave — When a dragged element departs
the drop target, it is called ondragleave.
5- ondragover — The dropped element is on top of the dragged element.
6- ondragstart — The user begins dragging an element.
7- ondrop — When a dragged element is dropped on a drop target,
it is called ondrop.
Keyboard Events:
1- onkeydown — When the user presses a key down
2- onkeypress — When the user begins to press a key.
3- onkeyup — A key is released by the user.
Frame Events:
1- onabort — The loading of a media is aborted with onabort.
2- onerror — When loading an external file, an error occurs.
3- onpagehide – When a user leaves a webpage, it is called onpagehide.
4- onpageshow — When the user navigates to a webpage
5- onhashchange — The anchor component of a URL has been changed.
6- onload — When an object has loaded
7- onresize — The document view gets resized when onresize is called.
8- onscroll — The scrollbar of an element is being
scrolled.onbeforeunload — Before the document is
due to be emptied, an event occurs.
9- onunload — When a page is emptied, this event occurs.
Animation Events:
1- animationstart — The animation in CSS has begun.
2- animationend — When a CSS animation is finished,
it is called animationend.
3- animationiteration — CSS animation is
repeated using animationiteration.
Clipboard Events:
1- oncut — The content of an element is cut by the user.
2- onpaste — When a user pastes material
into an element, it is called onpaste.
3- oncopy — The content of an element
is copied by the user.
Media Events:
1- onloadeddata — Media data has been loaded
2- onloadedmetadata — Metadata is
loaded (such as size and duration).
3- onloadstart — The browser begins
looking for the media that has been specified.
4- onabort — The loading of media has been halted.
5- onerror — When an error occurs while
loading an external file, the event onerror is triggered.
6- onpause — Media is paused, either
manually or automatically, by the user.
7- onplay — The video or audio has begun
or is no longer paused.
8- onstalled — The browser is attempting to
load the media, but it is not currently accessible.
9- oncanplay — The browser has the ability
to begin playing media (e.g. a file has buffered enough)
10- oncanplaythrough — The browser is capable
of playing media without pausing.
11- ondurationchange — The media's duration changes.
12- onended — The media's time has come to an end.
13- onsuspend — The browser is not loading media on purpose.
14- ontimeupdate — The situation has
shifted (e.g. because of fast forward)
15- onvolumechange — The volume of the media
has changed (including mute)
16- onwaiting — The media has taken a break, but
it is anticipated to resume soon (for example, buffering)
17- onplaying — Media that has been
paused or halted for buffering is now playing.
18- onprogress — The media is being downloaded by the browser.
19- onratechange — The media's playback speed changes.
20- onseeking — The user begins to move/skip.
Miscellaneous Events:
1- transitionend — When a CSS transition
is complete, this event is triggered.
2- onmessage — The event source has received a message.
3- onpopstate — When the history of the window changes
4- onshow — A <menu> element is shown as a
context menu when it is onshow.
5- onoffline — The browser switches to offline mode.
6- ononline — The browser enters the online mode.
7- ontouchcancel — The user's ability to
touch the screen has been halted.
8- ontouchstart — The touch-screen is
activated by placing a finger on it.
9- onstorage — An part of Web Storage has been upgraded.
10- ontoggle — The user toggles the details>
element open or closed.
11- onwheel — The mouse wheel moves up and
down when it passes over an element.
12- ontouchend — A touch-screen user's
finger is withdrawn.
13- ontouchmove — When a finger is dragged
over the screen, it is called ontouchmove.
Copy Code
Event propagation is a technique that governs
how events propagate or travel through the DOM
tree to reach their destination,
as well as what happens to them once they arrive.
The Capturing Phase:
<div onClick={() => console.log('outer div')}> //Run first
<div onClick={() => console.log('middle div')}> //Run second
<div onClick={() => console.log('innermost div')}> //Run Third
Click me!
</div>
</div>
</div>
The Bubbling Phase:
<div onClick={() => console.log('outer div')}> //Run Third
<div onClick={() => console.log('middle div')}> //Run second
<div onClick={() => console.log('innermost div')}> //Run first
Click me!
</div>
</div>
</div>Copy Code
try { // block of code to try
undefinedFunction();
}
catch(err) { // block to handle errors
console.log(err.message);
}
Throw error:
throw "My error message"; // throw a text
Input validation:
var x = document.getElementById("mynum").value; // get input value
try {
if(x == "") throw "empty"; // error cases
if(isNaN(x)) throw "not a number";
x = Number(x);
if(x > 10) throw "too high";
}
catch(err) { // if there's an error
document.write("Input is " + err); // output error
console.error(err); // write the error in console
}
finally {
document.write("</br />Done");/* executed regardless
of the try / catch result*/
}
Error name values:
RangeError: A number is "out of range"
ReferenceError: An illegal reference has occurred
SyntaxError: A syntax error has occurred
TypeError: A type error has occurred
URIError: An encodeURI() error has occurredCopy Code
function sum (a, b) {
return Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () { // send the response after 1 second
if (typeof a !== "number" || typeof b !== "number") {
return reject(new TypeError("Inputs must be numbers"));
}
resolve(a + b);
}, 1000);
});
}
var myPromise = sum(10, 5);
myPromsise.then(function (result) {
document.write(" 10 + 5: ", result);
return sum(null, "foo"); // Invalid data and return another promise
}).then(function () { // Won't be called because of the error
}).catch(function (err) { // The catch handler is called instead, after another second
console.error(err); // => Please provide two numbers to sum.
});
States:
pending, fulfilled, rejected
Properties:
Promise.length, Promise.prototype
Methods:
Promise.all(iterable), Promise.race(iterable),
Promise.reject(reason), Promise.resolve(value)Copy Code
let arr = [3, 4, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 3];
console.log("Array:", arr);
let test = [...arr];
test.length = 3;
console.log("Fix Length of Array 3", test);Copy Code
let arr = [3, 4, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 3];
let Sum = arr.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
console.log("Sum of Array:", Sum);
let Multiply = arr.reduce((a, b) => a * b);
console.log("Multiplication of Array;", Multiply);
let Subtract = arr.reduce((a, b) => a - b);
console.log("Subtraction of Array:", Subtract);
let Divide = arr.reduce((a, b) => a / b);
console.log("Division of Array:", Divide);Copy Code
let arr = [3, 4, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 3];
let unique = new Set(arr);
console.log(unique);
console.log("Remove Duplication of Array:", [...unique]);Copy Code
let x = 40;
x = ((x += 10), x);
console.log(x);Copy Code
let a1 = 10,
b1 = 20;
[a1, b1] = [b1, a1];
console.log(a1, b1);Copy Code
let arr = [3, 4, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 3];
function count_duplicate(arr) {
let counts = {};
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (counts[arr[i]]) {
counts[arr[i]] += 1;
} else {
counts[arr[i]] = 1;
}
}
for (let prop in counts) {
if (counts[prop] >= 2) {
console.log(prop + " counted: " + counts[prop] + " times.");
}
}
console.log(counts);
}
let temp1 = [...arr];
count_duplicate(temp1);Copy Code
let temp = [...arr];
temp.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log("Min Value:", temp[0], "Max Value:", temp[temp.length - 1]);Copy Code
let obj ={
name:"Abdullah Ansari",
city:{
name:"Lahore"
}
}
// DEEP COPY
let obj2=JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
obj2.name="Abdullah";
obj2.city.name="Karachi";
console.log("obj",obj)
console.log("obj2",obj2)Copy Code
let obj ={
name:"Abdullah Ansari",
city:{
name:"Lahore"
}
}
// SHAWLOW COPY
let obj2=obj;
obj2.name="Abdullah";
obj2.city.name="Karachi";
console.log("obj",obj)
console.log("obj2",obj2)
let obj3 ={
name:"Abdullah Ansari",
city:{
name:"Lahore"
}
}
//SPREAD OPEARATOR ONE LEVEL SHAWLOW COPY
let obj4=[...obj3];
obj4.name="Abdullah";
obj4.city.name="Karachi";
console.log("obj3",obj3)
console.log("obj4",obj4)Copy Code
let str="Abdullah Ansari";
console.log([str]);
console.log(str.split());Copy Code
let str="Abdullah Ansari";
console.warn(str.split(""));
console.log([...str]);Copy Code
let str="Abdullah Ansari";
console.warn(str.split(" "));Copy Code
let str="Abdullah Ansari";
console.log(str.split("n"));
/*The character is not in the array because we divide the
array on the behalf of that character*/Copy Code
let str="Abdullah Ansari";
console.log(str.replace("A","a"))